Innovation must be considered holistically – from the idea to implementation. This is because innovation development often fails not because of promising ideas, but rather because of a stringent process-related implementation. The focus should be on establishing the underlying business model.
From business idea to business model
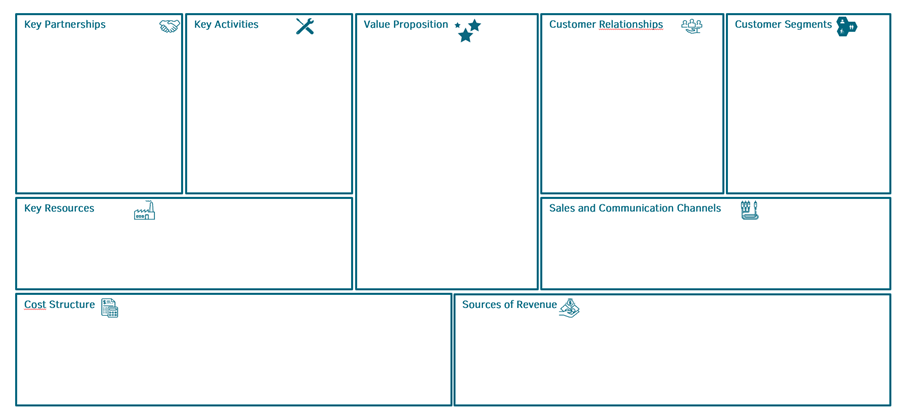
The Business Model Canvas serves as a “starting point” for the development and implementation of a business model and identifies various “patterns”. These include, for example, different customer segments. They require specific customer approaches before the appropriate business model can be defined and a corresponding strategy can be set up. To ensure that nothing is left to chance, the Business Model Canvas consolidates the most important questions into nine building blocks.

The 9 building blocks of the Business Model Canvas
1. Customer Segments
The focus on the needs of existing and potential customers is the central starting point for the building of the canvas model. If the customer segments differ greatly in their needs and are reflected in the structure of the product, it is advisable to design several business models and thus business model canvases.
2. Value Proposition
The value proposition is the core of the Business Model Canvas and must be clearly defined. Therefore, the following questions are helpful:
- What is the unique selling proposition? (What can the product do ten times better than others?)
- What problem does the product solve for customers?
- Why should customers buy especially this product?
3. Distribution and Communication Channels
In order for the product to reach the market, it is important to identify the buying behavior of the customers. This includes questions about how customers become aware of the product and how they can buy it. Considerations about which channels work best and how the selected channels interact best together also play an essential role.
4. Customer Relationships
The key question is: How are relationships built, maintained, and what efforts are made to retain customers and prevent them from leaving? Typical examples of customer loyalty are a personal contact person, self-service offers, assistance via chat or telephone, and much more. Important questions to ask yourself include:
- What customer relationships have I already created?
- How do my customer relationships fit with the rest of the business model?
- What are the costs of my customer relationships?
5. Revenue Sources
For any product or service, the most important question is: How do I make money from the product? To answer this question, a deeper look at revenue sources is necessary:
- For what benefits are customers willing to spend money?
- What is the preferred method of payment?
- What share do the respective revenue sources have among the total revenue?
6. Key Activities
To drive the business model forward, so-called key activities are necessary. These include actions that retain customers or acquire new ones. The focus should be on those activities which make the business model more successful, i.e. not a complete list of all activities, but only those which cannot be replaced.
7. Key Resources
Identifying resources critical to success is also necessary to build and sustain a business model. These include employees (Who is missing from the team?), infrastructure (What do I need to produce the product?) or intangible resources (e.g.: Do I need patents?).
8. Key Partnerships
Strategic partnerships can be essential for a successful business model. These include suppliers, vendors or technology partners. The focus should be on partnerships with strategic relevance, because if the partnership is easily replaceable, it is not a strategic relationship.
9. Cost Structure
The last block helps to identify the main cost drivers as well as costs. This block provides an overview of which expenses and costs are relevant to the business model. In doing so, we ask ourselves the following guiding questions:
- What resources/activities are particularly cost-intensive?
- What are the most important costs in our business model?
The Business Model Canvas is ready – now the practical test
The Business Model Canvas is a useful tool to realize where your product or idea stands, and which areas still need to be worked on.
It is important to understand the considerations for the individual areas as hypotheses that should be tested again and again under real conditions (through a “practical test”), such as customer surveys to verify the appropriate communication and sales channels or to identify new ones.
These considerations are especially important when it comes to convincing investors and / or strategic partners of the company’s own product or idea.
Using our own business model to drive forward the mobility of the future in a targeted manner
We firmly believe that in order to develop a sustainable, customer-centric mobility ecosystem of the future, intensive, cross-sector collaboration between traditional automotive manufacturers, infrastructure providers and the public sector is necessary. Through targeted collaborations and co-creation activities, we help our clients to take a holistic view on their business model(s), identify strategic partners and use this to expand the existing business model or derive new market opportunities.
If you are interested in working with the Business Model Canvas or if you need advice on innovation management and business model development, feel free to contact us!





 ISO/IEC 27001:2013 certified
ISO/IEC 27001:2013 certified