As we summarized in our article on major trends in the electricity market, the effect of decentralization in particular has a massive impact on the electricity market and its players.
One of the most promising business models counteracting the new challenges caused by the trends of decentralization & electrification is the introduction of smart grids.
The introduction of smart grids on the energy market
The term smart grid covers the communicative network and control of power generators, storage units, electrical consumers and network resources in energy transmission. This allows the monitoring and optimization of interconnected components. Overall the aim is to secure the energy supply based on an efficient and reliable system operation.
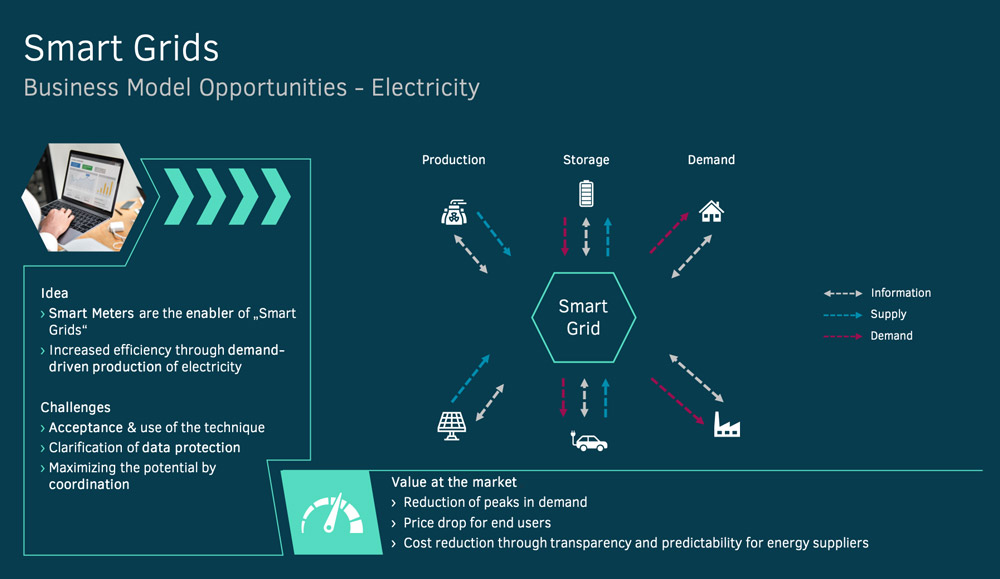
The basis for connecting electricity suppliers with multiple consumers is established by smart meters, which can measure both demand and supply of electricity in real time. Therefore smart meters can be described as intelligent electronic electricity meters, which serve as a communication platform for the control between power generation and consumption.
In the past, it was also technically possible to measure the power consumption of mass consumers (e.g. households) in real time. Nevertheless, only big consumers used this technology given the fact that the economic benefit was marginal.
However, this trend is currently changing with the distribution of smart meters across the EU, step by step enabling a smart control of the electricity demand side (e.g. smart home).
The rise of smart homes – Enabling a smart grid
The EU envisages that at least 80% of consumers will have a smart meter by the end of 2020. In addition to big energy companies, this rapid expansion in individual countries is also driven by municipals and telecommunication companies. Those three players can build above all on their experience with cable-based products such as electricity, cable TV and the Internet, as well as on their foray into new business fields such as “smart home”.
Regarding smart homes there are 4 key players offering this product to its customers:
- Energy companies
- Metering companies
- Smart home companies
- Telecommunication companies.
However, these companies are not necessarily in competition with each other, but act more as subsections in the big picture. As a consequence, this creates an enormous need to understand the different requirements and specifics of the respective industries, to respond to them and to coordinate all parties involved.
We from accilium see ourselves as an orchestrator enabling this crossectoral exchange. With our many years of experience in the energy and public sector, well-established specialists in the telecommunication industry, as well as a network to start-ups and scientific institutions, we strive to create added value for our customers in this field.
The article was published by Roman Salzgeber, accilium

 ISO/IEC 27001:2013 certified
ISO/IEC 27001:2013 certified